Urdu, which is one of the most developed modern Indian languages, has centuries-old history and a rich literary tradition. It has its origins in the western part of present Uttar Pradesh and areas around Delhi, but, unlike most of the other Indian languages, it is not confined to these areas or a single geographical area. The native Urdu speaking people are to be found all over the Indian subcontinent. The language also enjoys the status of one of the official languages of some of the provinces of India.
Its role in the promotion of cultural and communal harmony and in the freedom struggle of the country is well known. Urdu is one of the national languages under the 8th Schedule of the Indian constitution. Millions of people in northern India speak Urdu as their mother tongue. It is also largely used by the media as well as the entertainment industry. Currently, a large section of Indian society loves to learn and speak Urdu for understanding Urdu poetry and reading about the glorious history and culture of medieval India and also modern India.
Urdu, for millions of Indians, is not only a language but is an integral part of their cultural identity. Hindi and Urdu are generally considered to be one spoken language with two different literary traditions. That means that Hindi and Urdu speakers who shop in the same markets have no problems understanding each other -- they'd both say yeh kitne kaa hay for 'How much is it? And the Urdu one will be یہ کتنے کا ہے؟ Hindi is written from left to right in the Devanagari script, and is the official language of India, along with English.
Urdu, on the other hand, is written from right to left in the Nastaliq script and is the national language of Pakistan. It's also one of the official languages of the Indian states of Bihar and Jammu & Kashmir. Considered as one, these tongues constitute the second most spoken language in the world, sometimes called Hindustani. In their daily lives, Hindi and Urdu speakers communicate in their 'different' languages without major problems. Both Hindi and Urdu developed from Classical Sanskrit, which appeared in the Indus Valley at about the start of the Common Era.
The first old Hindi poetry was written in the year 769 AD, and by the European Middle Ages it became known as 'Hindvi'. Muslim Turks invaded the Punjab in 1027 and took control of Delhi in 1193. They paved the way for the Islamic Mughal Empire, which ruled northern India from the 16th century until it was defeated by the British Raj in the mid-19th century. It was at this time that the language of this book began to take form, a mixture of Hindvi grammar with Arabic, Persian and Turkish vocabulary. The Muslim speakers of Hindvi began to write in the Arabic script, creating Urdu, while the Hindu population incorporated the new words but continued to write in Devanagari script. In India, although Urdu is not and never was used exclusively by Muslims , the ongoing Hindi–Urdu controversy and modern cultural association of each language with the two religions has led to fewer Hindus using Urdu.
In part because the Pakistani government proclaimed Urdu the national language at Partition, the Indian state and some religious nationalists began to regard Urdu as a 'foreign' language, to be viewed with suspicion. Urdu advocates in India disagree whether it should be allowed to write Urdu in the Devanagari and Latin script to allow its survival, or whether this will only hasten its demise and that the language can only be preserved if expressed in the Perso-Arabic script. Urdu, which was often referred to by the British administrators in India as the Hindustani language, was promoted in colonial India by British policies to counter the previous emphasis on Persian. Urdu replaced Persian as the official language of India in 1837 and was made co-official, along with English. In contrast to Bihar, the struggle between Hindus, and Muslims over the status of Hindi and Urdu as the dominant regional language of U. P. was so prolonged that the overwhelming majority of the people of this state declared their mother tongue as either Hindi or Urdu in the 1961 mother tongue census.
Urdu Language Speaking States In India In Punjab, in contrast to the rest of North India before Independence, promoters of Hindi failed to get official acknowledgment for the language in that province where English and Urdu remained the official languages until Independence. In this period, the most important political struggle over language recognition was between Hindus and Muslims over the status of Hindi and Urdu. In this competition, Hindus whose mother tongue was Punjabi declared Hindi as their mother tongue in the censuses in order to gain a numerical benefit over Muslims and Urdu. Most Muslims, for their part, in fact spoke the various Punjabi dialects, though their political leaders fought to preserve official standing for Urdu. Paradoxically for Gandhi and his supporters, English represented a dividing force that emphasized the distance between educated Indian elites, who were more aligned with British colonizers, and non-English-speaking, often-uneducated masses. Gandhi maintained that to have a successful Independence movement was to govern through Indian ways, including through Indian regional languages.
During the late colonial period, Gandhi addressed audiences from 1916 to 1928 over English linguistic colonization in education. Hindustani, later known as a variety of Hindi and Urdu, is not commonly spoken across all of India, and it is considered a northern Indian regional language since it is distinct from the language families and scripts used in south India. English, therefore, served as a utilitarian language to connect disparate and diverse areas of the newly unified country, as it still does today. Now, Indian English, with a unique vocabulary and accent, is a recognized variety of English in the world. Today, there are twenty-eight states in India and eight union territories, or areas directly governed by the federal government, and each state has at least one official language and many have two, in addition to English. In this way, with unique languages and scripts attributed to each state, India often seems like a collection of distinct countries due to the cultural and linguistic differences between states.
Due to this vast diversity in languages and the way language is closely tied to identity, sometimes there are also struggles along religious and political lines that play out through language. Hindu nationalists engage in movements to spread the use of Hindi and Sanskrit as a means to spread the Hindu religion as well. Some have also felt that the distinct regional languages of states should indicate that people who do not speak those languages from birth should not be allowed to reside and work in states where they do not belong to the linguistic community. This was the message of the conservative party, the Shiv Sena, in Maharashtra. In this context, it can be said that Urdu may not be developed, but it is alive.
It is another matter that Urdu is constantly battling many deadly and dangerous diseases, the most important of which is hypocrisy and sectarianism, which itself It is present in the members of our own family. If we do not stand up for progress, our condition will be like that of a dead nation that has damaged its own dignity with its own hands, so we have to restore its lost dignity and brighten its horizons. The ground realities are that the use of Urdu at the governmental and educational levels has been completely restricted. When we demand the restoration of these rights of Urdu, we want the protection of the mother tongue of millions of people in this country and the restoration of these free use in educational institutions and offices at all levels that give them historical, moral and legal rights.
As always, but have been extraordinarily trampled on over the last fifty years. We clearly want the free use of Urdu at the governmental and educational levels in both majority and minority Urdu-speaking areas. In any case, we want to give our children an early education in their mother tongue. After that, they want the right to read Urdu as at least one language at every level and to establish Urdu medium institutions at every level.
This is the right that all other languages of the country have in this country and which we used to have but now it is being violated and there is no good reason for this injustice. However, despite our follow-up, the restoration of our linguistic rights is being delayed. In view of this situation, it is important for us to understand the point that the restoration of the rights of Urdu is closely related to all the things that have been stated in the program under review.
Achieving the objectives of this program can facilitate the restoration of Urdu rights. In the Delhi region of India the native language was Khariboli, whose earliest form is known as Old Hindi . It belongs to the Western Hindi group of the Central Indo-Aryan languages. The contact of the Hindu and Muslim cultures during the period of Islamic conquests and in the Indian subcontinent led to the development of Hindustani as a product of a composite Ganga-Jamuni tehzeeb. In cities such as Delhi, the Indian language Old Hindi began to acquire many Persian loanwords and continued to be called "Hindi" and later, also "Hindustani".
In southern India , a form of the language flourished in medieval India and is known as Dakhini, which contains loanwords from Telugu and Marathi. An early literary tradition of Hindavi was founded by Amir Khusrau in the late 13th century. From the 13th century until the end of the 18th century the language now known as Urdu was called Hindi, Hindavi, Hindustani, Dehlavi, Lahori, and Lashkari. The Turko-Afghan Delhi Sultanate established Persian as its official language in India, a policy continued by the Mughal Empire, which extended over most of northern South Asia from the 16th to 18th centuries and cemented Persian influence on Hindustani.
The name Urdu was first introduced by the poet Ghulam Hamadani Mushafi around 1780. While Urdu retained the grammar and core Indo-Aryan vocabulary of the local Indian dialect Khariboli, it adopted the Nastaleeq writing system – which was developed as a style of Persian calligraphy. Everyone have there culture and language we don't to be same for any development purpose also, development need not language.
The Urdu speaking populace's linguistic aspiration backed by Articles 29 and 30 of India's Constitution of India, 1950. The protection of the linguistic minority was ensured through the National Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities. Urdu was recognized as one of the languages under the eighth schedule of India's Constitution, 1950. There is no research in identifying the gap between the constitutional ideal and reality in inculcating Urdu languages officially and non-officially in India among the spoken linguistic minority.
But the Indian Constitution is not a self-enforcing document and requires the executive action and substantive infrastructure for compulsory educations in the Urdu language and mother tongue. However, despite the rise of the Muslim population, the Urdu speaking population did not rise proportionately over the last six decades. The paper takes a legal stance on the constitutional status of Urdu in India. Languages in India are categorized into language families based on their different linguistic origins, which often include different scripts as well. The main language families include Dravidian, Indo–Aryan, and Sino–Tibetan. Bodo is the Sino–Tibetan language spoken in northeastern Indian states with the most speakers (1.4 million).
Languages considered to be mother tongues or regional languages in the south of India have grammatical structures and scripts with Dravidian roots, and languages used in the central and northern regions of India are part of the Indo–Aryan family of languages. Many central and northern Indian languages use scripts derived from the Nagari script. Contemporary variations of Hindi use the Devanagari script, and scripts used in Gujarati, Punjabi, and Marathi use Nagari-derived scripts or versions of Devanagari that include some differences in their alphabets. Six languages also hold the title of classical languages , which are determined to have a history of recorded use for more than 1,500 years and a rich body of literature.
Furthermore, for a contemporary language to also be a classical language, it must be an original language and cannot be a variety, such as a dialect, stemming from another language. Just as there are many people who wish for their mother tongues to be recognized as official, scheduled languages, there are also efforts to add Indian languages to the list of classical languages. Once a language has the official status of a classical language, the Ministry of Education organizes international awards for scholars of those languages, sets up language studies centers, and grants funding to universities to promote the study of the language. Interestingly, the Constitution of India lists no national language for the country as a whole.
The Pakistani constitution proclaims Urdu to be a national language, which means that it is supposed to function as an instrument of national integration and as an exponent of the Muslim identity of Pakistani society. At the spoken level, Urdu is but the name used by Muslims for the Hindi language, but the script preferred by Muslims is the Persian Arabic, while that used by practically all Hindus is the Devanagari. The literary forms of the two languages are also diverge, with Hindi writers drawing from Sanskrit and Urdu writers drawing from Persian-Arabic sources in vocabulary and style. Urdu as an official language of the Union was overlooked in the Constituent Assembly after the partition of the country in 1947.
Urdu, which had been acknowledged up to Independence as an official language along with Hindi in U.P., also lost its place in that state in the Uttar Pradesh Official Language Act, 1951 in which Hindi was declared the one and only official language of the state. Although Urdu is listed in the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution, it is an official state language only in the small state of Jammu and Kashmir. In this way, the cultivation and practices of multilingualism in India lends itself to more than just a preservation of unique, regional identities but has great impact on how Indians interact with fellow Indians and much of the world. Multilingualism in India defines the nation within global and national networks and communities for business, education, and media. As language plays an important part in our daily interactions, multilingualism and linguistic diversity in India have shaped the country and unique cultural practices and policies within it.
Multilingualism in India has therefore played a key role in the country's contemporary politics. State boundaries were drawn along the lines of language groups, even though regions remain linguistically diverse, because languages in India can be an important way of defining one's identity. Many people in different Indian regions in cultural and religious groups retain distinct identities that set them apart from other communities through language. As India is culturally, ethnically, and religiously diverse, language is one way people maintain group identities.
Identity politics have also made mother tongues an object and mode of political struggle. Authors of the State Reorganization Act felt that democratic participation would grow if local populaces could access information and participate in government programs in their mother tongues. Language is a basis of identity and is why, when state boundaries were being redrawn after Independence in 1947, languages and the areas in which they were spoken were utmost factors of importance in where the boundaries of new Indian states would be.
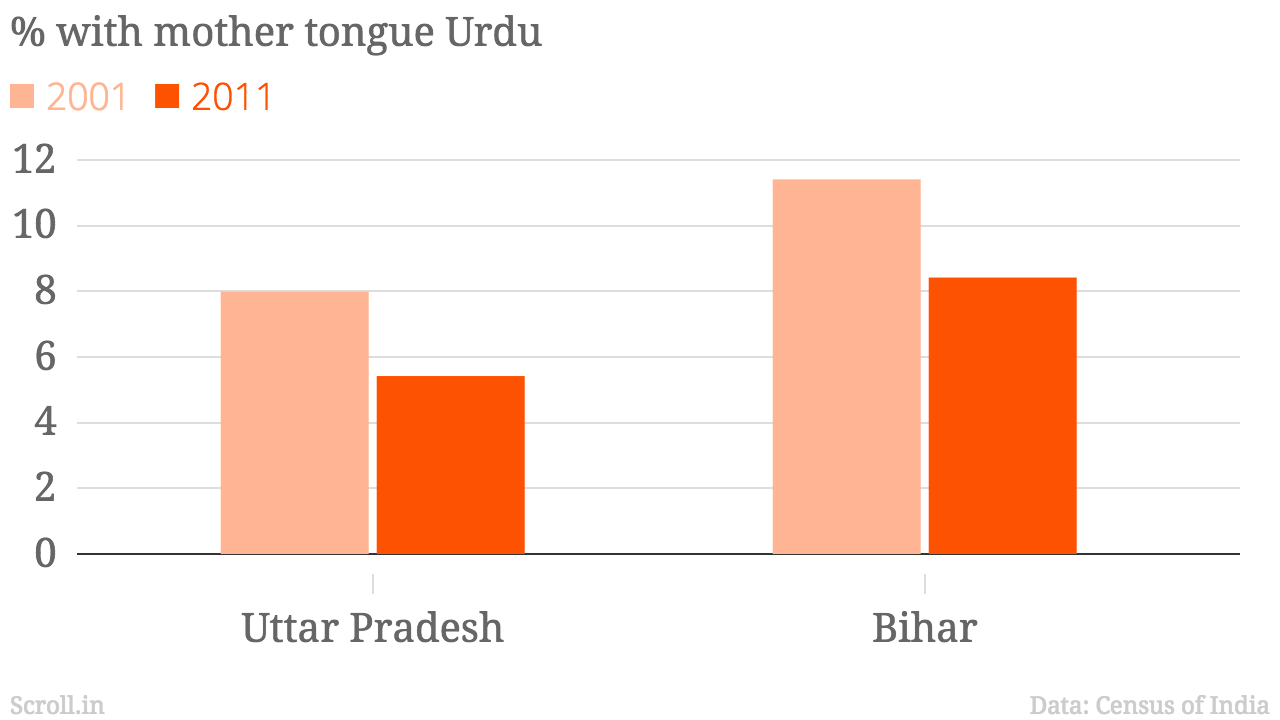
It is a major language in six states namely Uttar Pradesh , Bihar, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Jharkhand for a cumulative total 85.6 percent of Urdu population. In the Hindi belt Urdu is also widely spoken, in the other states like Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, Delhi and Utrakhand, unlike other national language. Its disadvantages are not having a home state in which it forms a majority. Nevertheless it has been designated as the second official language in several states like UP, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh apart from several smaller states. However, this status is largely a formality as far as official and educational use of Urdu is concerned. Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), the only state which recognizes Urdu as official language has a very minor Urdu population.
Urdu is the sole national, and one of the two official languages of Pakistan . It is spoken and understood throughout the country, whereas the state-by-state languages are the provincial languages, although only 7.57% of Pakistanis speak Urdu as their first language. Its official status has meant that Urdu is understood and spoken widely throughout Pakistan as a second or third language. It is used in education, literature, office and court business, although in practice, English is used instead of Urdu in the higher echelons of government.
Article 251 of the Pakistani Constitution mandates that Urdu be implemented as the sole language of government, though English continues to be the most widely used language at the higher echelons of Pakistani government. The Constitution is largely silent on the issue of a national language. The Eighth Schedule of the Constitution makes note of 22 regional languages, including Hindi. Hindi is limited to particular regions in the country — just like Bengali, Gujarati, Odia, or Kannada.
However, the confusion began when, under Article 343 of the Official Languages Act, Hindi in Devanagari script and English were designated as the "official languages" — that is, languages used for official correspondence. A comparison of Urdu and Hindi-speaking population in the non-Hindi speaking States has been made in Table VB. However, in non-Hindi speaking States as a whole, Urdu is spoken by a higher proportion of people of the State than Hindi. In major non-Hindi States like Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu, Urdu outranks Hindi.
Among all national languages Urdu and Sindhi are the only languages, which have no State base. Hindi, on the other hand, is the official language of the Union and also of 10 States . In 1973, Urdu was recognised as the sole national language of Pakistan – although English and regional languages were also granted official recognition. Finally, I agree with Ibn-e-Farid and Farouqui that self-help is best, that the Urduwallas will have to take the initiative and find the needed resources themselves. If Muslims can teach their children to vocalise the Qur'an, they can also simultaneously teach them to read Urdu. Where they have to fight against the prejudice of the authorities is in the area of primary education, which should be available to every child in his or her mother tongue.
That, unfortunately, has not been the case -- particularly in the so-called Hindi belt. There, even the facilities available in 1947 were deliberately destroyed by the official proponents of Hindi. The criminal damage they caused has not been corrected yet./4/ According to R. That is the only way they can successfully compete with their peers in these radically changing times. It is most heartening to note that the efforts of people like Hakim Abdul Hamid and Mr. A. R. Sherwani are directed in that direction and indeed bearing fruit.
During more than two hundred years of British rule, shifting winds of patronage changed the linguistic landscape immensely. It was during the colonial period that the Indian public became more invested in language politics, and began to promote Hindi and Urdu as distinct languages, distinguished not only by orthography, but on a more fundamental level, as markers of cultural identity. Some even engaged in language debates and sought to "purify," standardize, and garner institutional recognition of "their" language. With independence and Partition in 1947, Hindi became the official language of India, and Urdu the official language of Pakistan, though one of the ironies of this history is that more people claim Urdu as their first language in today's India than in Pakistan.




























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.